Tags and keywords
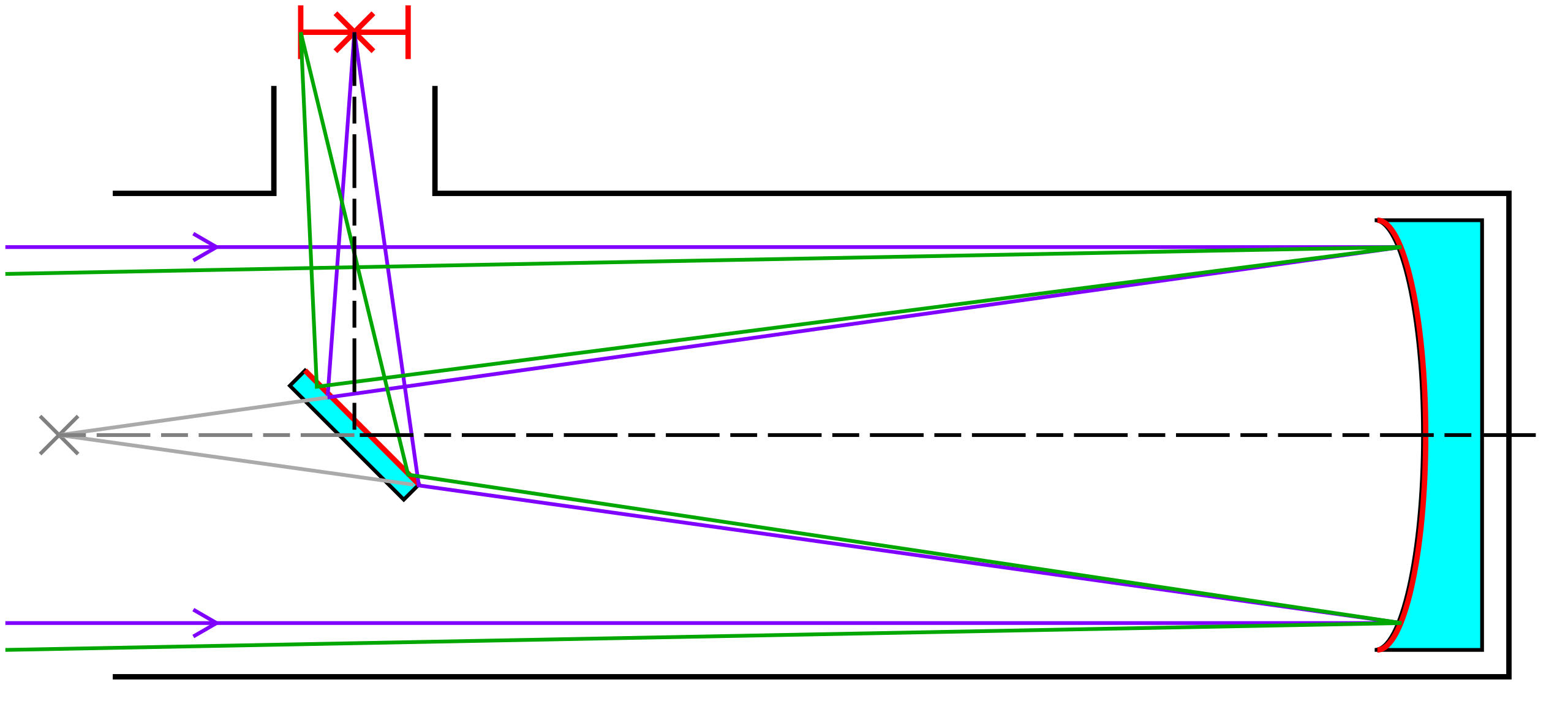
Any NewtonianReflector is characterised by having a FlatMirror as its secondary, but there are two types, the ParabolicNewtonianReflector with a concave ParabolicMirror as primary and the SphericalNewtonianReflector with a concave SphericalMirror as primary.
One snippet refers to a 'telescope tube'. It is assumed here that any ReflectingTelescope has exactly one part property tube:Tube[1], although this name glosses over the details somewhat. In the 17th century there were refractors called aerial telescopes used by the Huygens brothers that had two short tubes and a large air gap to achieve long focal lengths, with the two short tubes connected by taught strings. Some collapsible Dobsonian mount Newtownian reflectors have more of a cage-like truss tube.
Because the part property tube:Tube[1] has AggregationKind composite it is directly involved in the part/assembly composition hierarchy. We'll see later how it will in turn compose assemblies for the primary mirror, secondary mirror, eyepiece etc.
Light has to get in an out of the Tube, so it has ports iLight and oLight (this will also serve fine for the hole behind the hole of the primary mirrors of Gregorian and Cassegrain reflectors).
We also have a new ValueType FocalRatio and a value property fRatio:
Because focalLength is "optional" (not necessarily applicable) for every kind of OpticalElement, the multiplicity of fRatio in OpticalElement is [0..1], whereas in OpticalTelescope it is fRatio:FocalRatio[1]. Note how OpticalTelescope has now also been given a diameter {aka="aperture"}.
And one snippet refers to 'high visual resolution', which suggests a ValueType VisualResolution and OpticalTelescope now has a value property resolution:VisualResolution, although it is not specified what resolution counts as "high".


